ExecuteDataReader
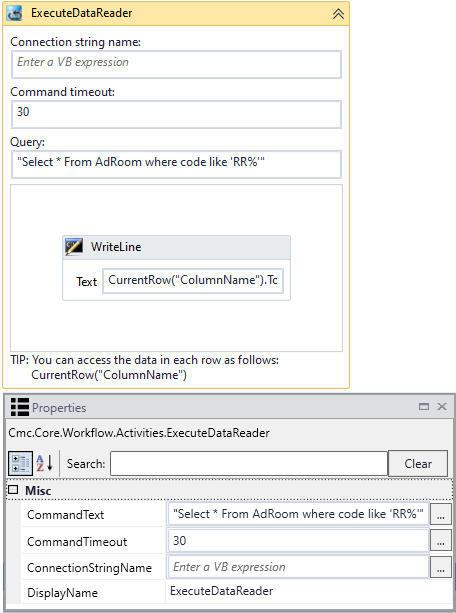
The ExecuteDataReader activity enables you to create workflows that perform two steps:
- Execute an SQL query.
- Execute activities in the query result.
If the query successfully connects to the data source, it queries the database and executes the activities in the body once per data row returned.
|
|
In general, the connection strings used during workflow execution are retrieved from the web.config of the product that triggers workflow execution. Only if you want to run a workflow with ExecuteDataReader, ExecuteNonQuery, or ExecuteQuery activity in test mode using the Run option in Workflow Composer, would you need to manually add the connection string to the Workflow Composer web.config file. |
Properties
| Property | Value | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CommandText | InArgument<String>
|
Yes | Enter a command that specifies the query to perform on the target data source
and is expected to return a result set. Note: Supply an SQL query that will only return one set of rows from one table. Do not attempt to return multiple sets of data since this activity will only utilize the first set of data rows returned. Example
|
| CommandTimeout | InArgument<Int32>
|
No | You can adjust the CommandTimeout value if the activity needs to execute long-running SQL statements. The default and minimum command timeout is 30 seconds. The maximum is 1800 (30 minutes). |
| ConnectionStringName | InArgument<String>
|
No | Enter the name of a connection string that has been configured in the CONFIG file of the host application that is executing the workflows (see Connection Strings).
If none is specified, this activity attempts to connect to a connection string named Note: Forms Builder 3.6 introduces the "CrmConnection" string in the web.config of Forms Renderer (see Renderer Connection Strings). If you have created workflows with ExecuteDataReader activities, ensure that connection strings in the activities match the updated web.config of Forms Renderer. |
| DisplayName | String
|
No | Specify a name for the activity or accept the default. |
ExecuteDataReader Example 1
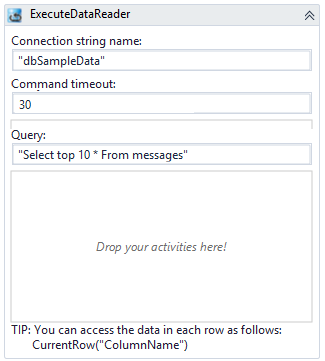
This example retrieves rows from the database and writes the results to the console.
-
Open a workflow or create a new workflow.
-
Drag the ExecuteDataReader activity into your workflow.
-
Specify the values for the input arguments or map them to workflow variables.
-
Add activities into the body of this activity.
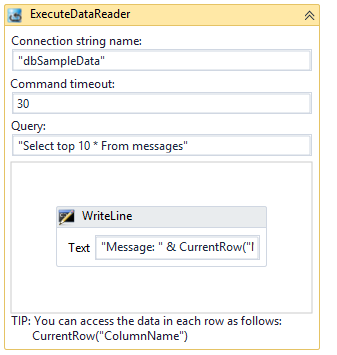
Tip: The activities in the body of this activity will be executed once per every row returned from the database query.
You can access the data in each row as a variable called
CurrentRow.You can then use the data in each row using the format:
CurrentRow(“ColumnName”). -
Run the workflow.
Result:
The query successfully connects to the data source, queries the database, and executes the activities in the body once per data row returned.
ExecuteDataReader Example 2
This example retrieves a value from a single row in the database and uses the retrieved value in an assignment statement.
-
Open a workflow or create a new workflow.
-
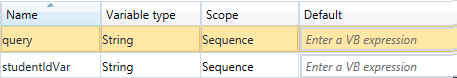
Create two variables to hold the query statement and the value retrieved from the database.
- query
- studentIdVar
-
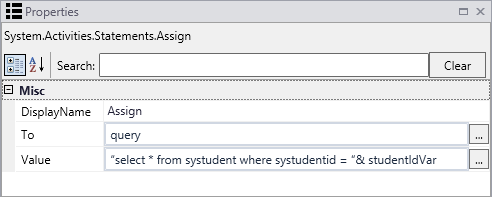
Drag an Assign activity into a sequence.
Assign the following value to a string named query:
“select * from systudent where systudentid = “& studentIdVar
-
Drag the ExecuteDataReader activity into your sequence.
-
In the Query field of the ExecuteDataReader activity, specify query (the name of the string assigned in the previous step).
-
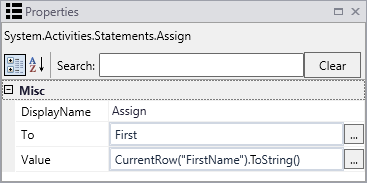
Drop an Assign activity into the body of the ExecuteDataReader activity.
Assign the following value to a string named First:
CurrentRow("FirstName").toString()
Note:
The data type returned by the query must be specified in the assignment.
-
To get a string field value from a database row, the expression.ToString() is needed.
-
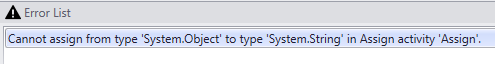
To get an integer value, the assignment would be like this: Convert.ToInt32(CurrentRow(“dbIntegerField”))
Without the type conversion, the assignment statement fails with the following error:
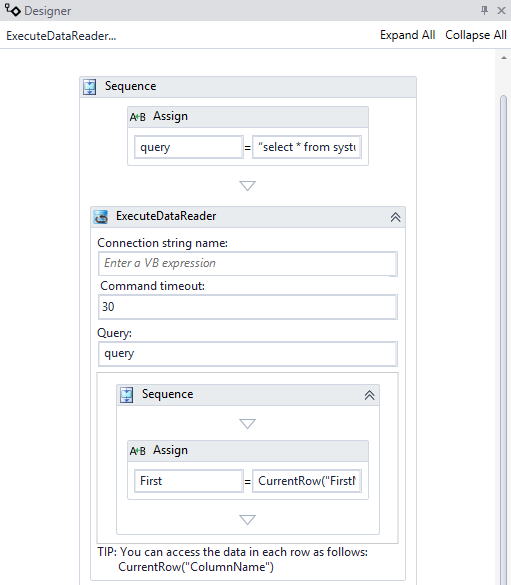
The following image shows the completed workflow section:
-
ExecuteDataReader Example 3
The following example uses the ExecuteDataReader activity in the context of a Forms Builder sequence. The form sequence prompts the user to enter his/her contact details, select a program, and e-sign an enrollment agreement.
-
The LookupUser activity captures the UserName from the formInstance.UserName argument and returns the studentid.
-
The GetEntity activity takes the studentid value and returns the studentEntity value.
-
Two Assign activities associate the student name and address fields of the studentEntity with values passed from the form sequence via the StudentName and Address arguments.
-
The third Assign activity associates the DeliveryMethod argument from the form sequence with the DeliveryMethodText variable in the workflow. The variable can be assigned a default string, e.g., "Program is blended (hybrid) including on-ground and online delivery".
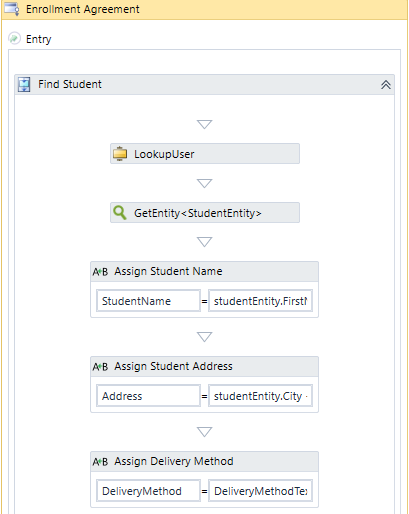
-
The ExecuteDataReader runs the following query on the Anthology Student database to retrieve the enrollment ID for the student ID:
"select adenrollid from adenroll where systudentid = " & studentid
In Anthology Student, the adenrollid from the AdEnroll table is used as the enrollment identifier if an applicant record is converted to an enrollment record.
-
The Assign activity within in the ExecuteDataReader assigns the following value to the EnrollID:
DirectCast(CurrentRow("adenrollid"), int32)
-
The GetEntity activity below the ExecuteDataReader uses the EnrollID value to retrieve the ApplicantEntity.
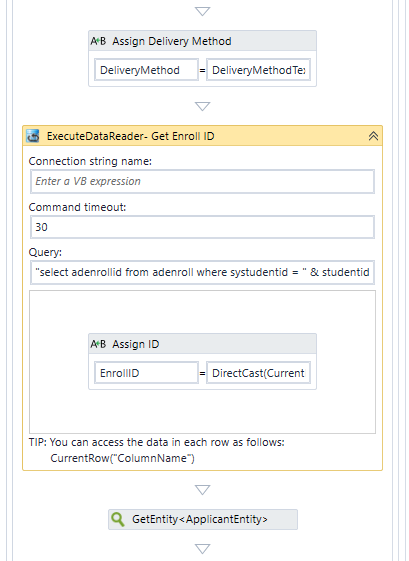
-
Next, the workflow retrieves the enrollment agreement document for the student from the database, presents the document to the student for e-signature, and saves the signed document.
For more examples of workflows with ExecuteDataReader, see:
The ExecuteDataReader activity enables you to create workflows that perform two steps:
- Execute an SQL query.
- Execute activities in the query result.
If the query successfully connects to the data source, it queries the database and executes the activities in the body once per data row returned. For more information, see ExecuteDataReader Example 1.
|
|
In general, the connection strings used during workflow execution are retrieved from the web.config of the product that triggers workflow execution. Only if you want to run a workflow with ExecuteDataReader, ExecuteNonQuery, or ExecuteQuery activity in test mode using the Run option in Workflow Composer, would you need to manually add the connection string to the Workflow Composer web.config file. |
Properties
| Property | Value | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CommandText | InArgument<String>
|
Yes | Enter a command that specifies the query to perform on the target data source
and is expected to return a result set. Note: Supply an SQL query that will only return one set of rows from one table. Do not attempt to return multiple sets of data since this activity will only utilize the first set of data rows returned. Example
|
| ConnectionString | InArgument<String>
|
No | Enter the name of a connection string that has been configured in the CONFIG file of the host application that is executing the workflows (see Connection Strings).
If none is specified, this activity attempts to connect to a connection string named “DbConnection”. Connection String Example
|
| DisplayName | String
|
No | Specify a name for the activity or accept the default. |
This example retrieves rows from the database and writes the results to the console.
-
Open a workflow or create a new workflow.
-
Drag the ExecuteDataReader activity into your workflow.
-
Specify the values for the input arguments or map them to workflow variables.

-
Add activities into the body of this activity.

Tip: The activities in the body of this activity will be executed once per every row returned from the database query.
You can access the data in each row as a variable called
CurrentRow.You can then use the data in each row using the format:
CurrentRow(“ColumnName”). -
Run the workflow.
Result:
The query successfully connects to the data source, queries the database, and executes the activities in the body once per data row returned.
This example retrieves a value from a single row in the database and uses the retrieved value in an assignment statement.
-
Open a workflow or create a new workflow.
-
Create two variables to hold the query statement and the value retrieved from the database.
- query
- studentIdVar

-
Drag an Assign activity into a sequence.
Assign the following value to a string named query:
“select * from systudent where systudentid = “& studentIdVar

-
Drag the ExecuteDataReader activity into your sequence.
-
In the Query field of the ExecuteDataReader activity, specify query (the name of the string assigned in the previous step).
-
Drop an Assign activity into the body of the ExecuteDataReader activity.
Assign the following value to a string named First:
CurrentRow("FirstName").toString()

Note:
The data type returned by the query must be specified in the assignment.
-
To get a string field value from a database row, the expression.ToString() is needed.
-
To get an integer value, the assignment would be like this: Convert.ToInt32(CurrentRow(“dbIntegerField”))
Without the type conversion, the assignment statement fails with the following error:

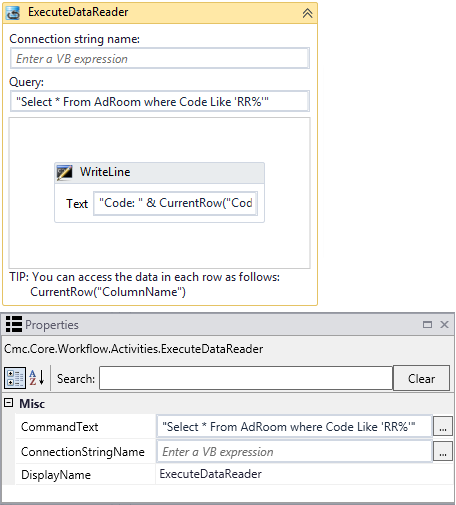
The following image shows the completed workflow section:

-
To see how ExecuteDataReader can be used in a workflow, refer to:
The ExecuteDataReader activity enables you to create workflows that perform two steps:
- Execute an SQL query.
- Execute activities in the query result.
If the query successfully connects to the data source, it queries the database and executes the activities in the body once per data row returned. For more information, see ExecuteDataReader Example 1.

|
|
In general, the connection strings used during workflow execution are retrieved from the web.config of the product that triggers workflow execution. Only if you want to run a workflow with ExecuteDataReader, ExecuteNonQuery, or ExecuteQuery activity in test mode using the Run option in Workflow Composer, would you need to manually add the connection string to the Workflow Composer web.config file. |
Properties
| Property | Value | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CommandText | InArgument<String>
|
Yes | Enter a command that specifies the query to perform on the target data source
and is expected to return a result set. Note: Supply an SQL query that will only return one set of rows from one table. Do not attempt to return multiple sets of data since this activity will only utilize the first set of data rows returned. Example
|
| ConnectionString | InArgument<String>
|
No | Enter the name of a connection string that has been configured in the CONFIG file of the host application that is executing the workflows (see Connection Strings).
If none is specified, this activity attempts to connect to a connection string named “DbConnection”. Connection String Example
|
| DisplayName | String
|
No | Specify a name for the activity or accept the default. |
This example retrieves rows from the database and writes the results to the console.
-
Open a workflow or create a new workflow.
-
Drag the ExecuteDataReader activity into your workflow.
-
Specify the values for the input arguments or map them to workflow variables.

-
Add activities into the body of this activity.

Tip: The activities in the body of this activity will be executed once per every row returned from the database query.
You can access the data in each row as a variable called
CurrentRow.You can then use the data in each row using the format:
CurrentRow(“ColumnName”). -
Run the workflow.
Result:
The query successfully connects to the data source, queries the database, and executes the activities in the body once per data row returned.
This example retrieves a value from a single row in the database and uses the retrieved value in an assignment statement.
-
Open a workflow or create a new workflow.
-
Create two variables to hold the query statement and the value retrieved from the database.
- query
- studentIdVar

-
Drag an Assign activity into a sequence.
Assign the following value to a string named query:
“select * from systudent where systudentid = “& studentIdVar

-
Drag the ExecuteDataReader activity into your sequence.
-
In the Query field of the ExecuteDataReader activity, specify query (the name of the string assigned in the previous step).
-
Drop an Assign activity into the body of the ExecuteDataReader activity.
Assign the following value to a string named First:
CurrentRow("FirstName").toString()

Note:
The data type returned by the query must be specified in the assignment.
-
To get a string field value from a database row, the expression.ToString() is needed.
-
To get an integer value, the assignment would be like this: Convert.ToInt32(CurrentRow(“dbIntegerField”))
Without the type conversion, the assignment statement fails with the following error:

The following image shows the completed workflow section:

-
To see how ExecuteDataReader can be used in a workflow, refer to: